Email
info@lgsc.co.uk
Email
info@lgsc.co.uk
Phone
0203 312 6130
Location
The Lindo Wing, St Mary’s Hospital,
Praed Street, London W2 1NY
Appendicitis means inflammation of the appendix. The reason why the appendix becomes inflamed is not known in most cases. It is suspected that the residual food material or hard stool get stuck in the appendix and blocks it. The blocked appendix gets inflamed and infected by germs (bacteria).
The inflamed appendix gradually swells and fills with pus. Eventually, if not treated, the swollen appendix might burst (perforate). This is very serious, as the contents of the intestine then leak into the tummy (abdominal) cavity. This can cause a serious infection of the membrane that lines the abdomen (peritonitis), or a collection of pus (an abscess) in the abdomen. So, if appendicitis is suspected, early treatment is best before it bursts.
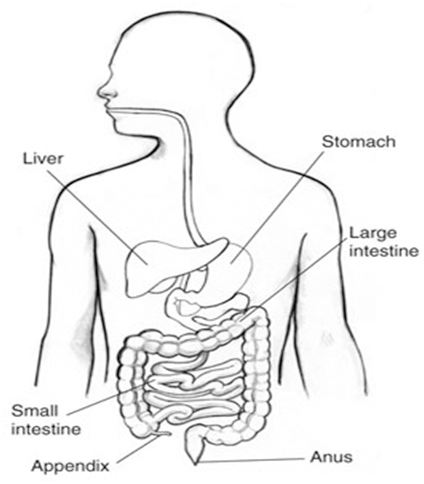
The appendix is a 5-10 cm small, mobile, dead-end pouch, worm-like structure, which comes off the wall of large bowel (intestine) at the star. It does not seem to play any significant function in digestion process. The small bowel digests and absorbs nutrients from food. The residual fibers and unabsorbed food material is passed through large bowel and eventually secreted as faeces.
Appendicitis commonly presents with tummy (abdomen) pain, which starts in the middle and is localized to the right lower side of the abdomen. It is often associated with being sick (vomiting). Any movement is painful and you won't want to move around at all. The severity of pain may vary according to the position of the appendix and if there is perforation. You become very ill as you develop serious infection of the membrane that lines the whole abdomen. Other symptoms include raised temperature (fever), diarrhoea, constipation, and frequently passing urine.
You will be admitted to hospital if appendicitis is suspected. There is no easy and foolproof test to confirm appendicitis. It depends on whether the symptoms and also the findings when you are examined suggest that appendicitis is the probable diagnosis. Blood tests and imaging tests, an ultrasound or CT scan, are often used to help decide on the diagnosis. By the time investigations are carried out, antibiotics are given.
An operation to remove the inflamed appendix is usually done quite quickly once the diagnosis is made. It is much better to remove an inflamed appendix before it bursts (perforates). Removal of the appendix is one of the most commonly performed operations in the UK.
Surgery is commonly done by a keyhole operation, as the recovery is quicker compared to having an open operation. Sometimes keyhole surgery isn't recommended and open surgery is performed instead. This is likely to be needed if the appendix has already burst and formed a lump called an appendix mass.

Please note, most insurance policies in the UK do not cover weight-loss surgery. However, we will do our utmost to provide the best package for you should you choose to have your surgery with us.
The contents on this site is for information only, and is not meant to substitute the advice of your own physician or other medical professional.